Light Receptors Which See Best at Night Are the Cones
We have cones that pick up light waves for red green and blue. Two important types are rods and cones.
Photoreceptors American Academy Of Ophthalmology
A beam of light that contains mostly short-wavelength blue radiation stimulates the cone cells that respond to 430-nanometer light to a far greater extent than the other two cone types.
. The sensitivity of rods to photons of light. This is 70 percent of all the sensory receptors in your entire body for touch taste smell hearing and sight all put together. Rods are extremely sensitive and form the basis for scotopic vision vision in dim light.
Although not as energetic as ultraviolet UV light there is concern that high doses of blue light may cause more cellular damage than longer wavelengths of visible light. To see best at night look just above or below the objectthis keeps the image on the rods. As the light hits the eye the cornea bends the.
Cones enable us to see in dim light. Rods provide color vision. For humans to see an object light first must bounce off that object and towards our eye.
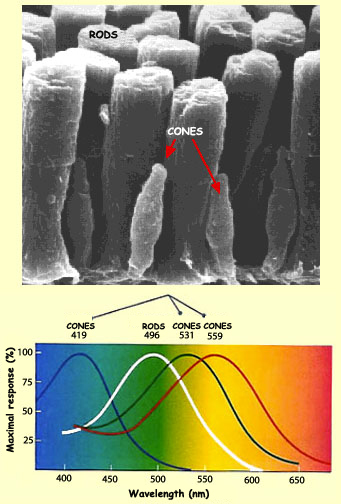
Rods which contain the visual pigment rhodopsin are better for night vision because they are sensitive to small quantities of light. Cones that code for green response maximally to 533 nm and are referred to as M or medium wavelength receptors and red codes respond maximally to 564 nm and are referred to a L or long. In dim light the receptors in your eyes called rods are doing most of the work.
Animals that are able to see visible light have different ranges of color perception. Cones on the other hand provide us with the ability to see color and fine detail when the light is brighter. Humans can see objects clearly at 100 to 200 feet 30 to 60 meters away.
Cones for day vision and rods for night vision. Cones allow us to see colour spatial detail and motion at light levels typical for daytime. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400700 nanometres nm corresponding to frequencies of 750-420 terahertz between the infrared with longer wavelengths and the ultraviolet with shorter.
Blue light is the visible light at the blue end of the spectrum. Stimulation of combinations of the three types of cones. For example blue cones are most sensitive to reflected light of 437 nm for this reason these receptors are referred to as S or short-wavelength receptors.
Of course you cannot see if it is completely dark but you can see a bit in dim light. Cones are less sensitive but allow for color vision in photopic vision or vision in bright light. Rods provide higher visual acuity than do cones.
The different varieties of retinal in each cone type. There are two sorts of light receptors in a birds eye rods and cones. This is possible because we have two receptors in our eyes.
At this point colors disappear and we can. Red green or blue cones respond best to those colors of light. These are the rods and the cones.
There are three types of cones differing in their preference for light at specific wavelengths Fig. Rods and cones all have the same kind of opsin. Cones detect specific colours or wavelengths of light so they are more important to colour-orientated animals such as birds.
Rods are more prevalent near the edges of the retina. Cones vary in their spectral sensitivity. This beam will activate the blue color pigment.
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation within the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is perceived by the human eye. C Seeing In Color - we can see many colors but only have 3 types of cones that receive information about color. Below about 1 Lux our rods become active.
Each human retina and you have two one in each eye contains 125 million rods and about 6 million cones. Rods require brighter light to activate them than do cones. The cones are mostly in and around the fovea but decrease as you go out.
The ability to see many different color variations results from. The other photoreceptors in your eye called cones are the ones that are used for seeing color. The long-wavelength-sensitive cones L cones the medium-wavelength-sensitive cone M cones and the short-wavelength-sensitive cones S cones.
However the rods do not provide any information about color. Rods and cones differ in their distribution across the retina with the highest concentration of cones found in the fovea the central region of focus and rods dominating the periphery see Figure 2. Humans also can see with much greater resolution with a greater range of vibrant colors thanks to their eyes many cones.
The light-sensing cells on the retina are known as photoreceptors. Stimulation of combinations of the three types of rods. Cones are found in highest density in the fovea.
Humans have three different types of color receptors cones resulting in a trichromatic organization of color whereas most birds have four different types of cones resulting in a tetrachromatic experience including gray blue green and red.

Comments
Post a Comment